Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common but serious oral health condition that affects the gums and supporting structures of the teeth. If left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss and other health complications. Understanding the symptoms early can help in seeking timely treatment and preventing further damage.
What Is Gum Disease?
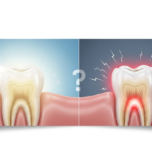
Gum disease is an infection caused by bacteria in dental plaque. When plaque accumulates along the gumline, it leads to inflammation, which, if untreated, progresses from gingivitis to periodontitis.
Early Symptoms of Gum Disease
Gum disease often starts with mild symptoms, which can be easy to overlook. Some early warning signs include:
- Red or swollen gums – Inflammation is one of the first signs of gum disease.
- Bleeding gums – Gums that bleed while brushing or flossing indicate an issue.
- Bad breath (halitosis) – Persistent bad breath can be a sign of bacterial infection.
- Tender gums – Gums may feel sore or sensitive when touched or while eating.
- Receding gums – Gums pulling away from the teeth is an indication of worsening gum disease.
Advanced Symptoms of Periodontal Disease
As gum disease progresses, symptoms become more severe. These include:
- Loose or shifting teeth – The infection weakens the bone supporting the teeth.
- Pain while chewing – Advanced gum disease can make eating painful.
- Pus between the gums and teeth – A sign of infection that requires urgent care.
- Gum abscesses – Pockets of infection may form, leading to swelling and discomfort.
- Changes in bite alignment – As teeth loosen, they may shift out of position.
Risk Factors for Developing Gum Disease
Several factors can increase the risk of developing periodontal disease, such as:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Smoking or tobacco use
- Diabetes
- Hormonal changes (pregnancy, menopause)
- Genetic predisposition
- Certain medications that reduce saliva flow
How to Prevent Gum Disease
Preventing gum disease is easier than treating it. Some effective prevention tips include:
- Brushing and flossing daily – Remove plaque and food debris regularly.
- Regular dental check-ups – Early detection can prevent progression.
- Maintaining a healthy diet – Avoid sugary foods that promote bacterial growth.
- Quitting smoking – Tobacco use is a major risk factor for gum disease.
- Using an antibacterial mouthwash – Helps reduce bacteria buildup.
When to See a Dentist?
If you experience persistent gum irritation, bleeding, or bad breath, it’s essential to visit a dentist as soon as possible. Early treatment can prevent irreversible damage and improve overall oral health.
Conclusion
Gum disease is a serious but preventable condition. By recognizing the early symptoms and taking proactive steps, you can maintain healthy gums and prevent complications. Regular dental visits and good oral hygiene habits play a crucial role in keeping periodontal disease at bay.